Revit Interface and Terminology
Exploring the Revit Interface, Terminology, and Sketching
Venturing into the amazing world of Revit Architecture can be simultaneously exhilarating and daunting, particularly for newcomers to the software. To provide you with a solid foundation, let's get into the nuances of the Revit interface, terminology, and sketching techniques.
Revit 2024 Interface, Terminology, and Sketching
We can definitely help you with basic to advanced lessons on Autodesk Revit, focusing on key concepts and providing explanations along with images where needed. Revit is a Building Information Modeling (BIM) software, widely used in the fields of architecture, engineering, and construction to design buildings and structures with a sophisticated approach.
Here's an outline of what a basic Revit lesson we might cover:
Introduction to Revit
- Overview of BIM and its importance
- Basic Revit interface and navigation
Starting a New Project
- How to start a new project
- Understanding Revit templates
Basic Modeling Tools
- Creating walls, doors, and windows
- Adding floors, ceilings, and roofs
View Management
- Working with different types of views (plan, section, elevation)
- Managing view properties and visibility settings
Components and Families
- Introduction to Revit families and components
- Loading and placing components
Dimensioning and Annotation
- Adding dimensions and text notes
- Creating and modifying tags
Basic Schedules
- Generating schedules
- Customizing schedule appearances
For each of the topics listed, we will offer a concise explanation accompanied by an illustrative image to clarify the discussed concept or feature. Should you require further details or additional images pertaining to any particular area, feel free to explore the advanced lessons sections where we get deeper into each topic.
Revit 2024 User Interface
By familiarizing themselves with the components and functionalities of the Revit 2024 user interface, architects, engineers, designers, and construction professionals can streamline their workflow, enhance productivity, and bring their architectural visions to life with confidence and precision.
If you are new to the Revit Architecture environment, this introduction is a good start. Here is a terminology of the various Revit Architecture tools and function.
- Tutorial 1
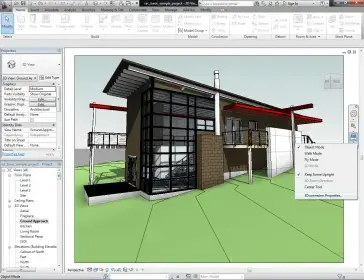
When you open Revit Architecture, you see a window that looks like the image shown here.
Working through the exercises, you will be performing functions such as:
- Using the menus.
- Using the design bar tools to add things to the project.
- Using the toolbar tools to modify things with Copy, Move, Align, and Split tools.
- Using the project browser to change views or set views current.
Menu System:
When you first launch Revit Architecture, you'll encounter a comprehensive menu system that serves as your gateway to a myriad of commands and functions. From the File menu, where you can create new projects or open existing ones, to the View menu, which allows you to adjust display settings and perspectives, each menu item offers a wealth of options to explore and utilize in your architectural endeavors.
Click the menu item to view a list. Many of the menu functions have flyout functions as well.
Toolbars:
Directly below the menu system, you'll find a set of toolbars that provide quick access to essential functions and tools. Here, you'll discover familiar commands such as New, Open, Save, and Print, as well as tools for modifying elements within your project, such as Copy, Move, and Trim. These toolbars streamline your workflow, enabling efficient navigation and execution of tasks.
Design Bar:
Situated on the left side of the drawing window, the design bar acts as your primary toolkit for adding components and elements to your project. From walls and doors to windows and furniture, each tab within the design bar offers a curated selection of tools tailored to specific architectural tasks. Whether you're creating a floor plan, elevation, or section view, the design bar provides the necessary resources to bring your vision to life.
Options Bar:
Located below the toolbar, the options bar offers a dynamic interface for adjusting properties and settings while working on your project. As you select different tools and commands, the options bar adapts to display relevant parameters and options, allowing you to fine-tune your designs with precision and efficiency. Paying close attention to the options bar ensures that you have full control over the elements you create and manipulate within your project.
Revit Architecture Workflow:
Mastering the workflow in Revit Architecture is essential for efficient project execution. When adding objects to your project, you'll follow a structured sequence: first, select the desired object from the design bar; next, adjust its properties and settings using the options bar; finally, implement the object in the drawing window. While this workflow provides a systematic approach to project development, it's important to remain flexible and adapt your process as you gain familiarity with the software.
Revit Architecture Status Bar:
Located at the lower-left corner of the screen, the status bar serves as a valuable indicator of your current actions and selections. Whether you're adding objects or modifying elements, the status bar provides real-time feedback, guiding you through each step of the process. By monitoring the status bar, you can stay informed and confident in your interactions with the software.
Revit Architecture Workspace View Bar:
Near the bottom-left side of the screen, the Workspace View Bar offers additional controls and options for managing your project views. From adjusting plotting scales to controlling detail levels, this toolbar provides valuable tools for optimizing your workspace and enhancing your productivity. Additionally, functions for hiding or isolating objects in the current view empower you to focus on specific elements and aspects of your design.
Project Browser:
Positioned between the design bar and the drawing area, the project browser serves as your central hub for navigating and managing project components. Organized in a hierarchical tree structure, the project browser presents a comprehensive overview of your project views and families (building component definitions), allowing you to access and manipulate them with ease. By leveraging the project browser, you can streamline your workflow and maintain efficient project organization.
By acquainting yourself with the Revit interface, terminology, and sketching techniques outlined above, you'll be well-equipped to start your architectural journey with confidence and clarity. As you continue to explore the vast capabilities of Revit Architecture, remember to embrace curiosity and creativity, as they are the driving forces behind innovation and excellence in architectural design.
Revit Questions & Answers
Navigating the intricacies of Revit's interface is crucial for mastering the software and optimizing your workflow. Let's get into some common questions about the interface in Revit and explore detailed answers to each query.
What is Revit used for?
Revit is a powerful Building Information Modeling (BIM) software developed by Autodesk, primarily used by architects, engineers, designers, and construction professionals for creating, visualizing, and documenting building projects.
Revit allows users to design buildings and structures in 3D, incorporating elements such as walls, doors, windows, roofs, and structural components. The software facilitates collaboration among project stakeholders, enabling seamless communication and coordination throughout the design and construction process.
Additionally, Revit offers tools for generating detailed drawings, schedules, and documentation, streamlining the workflow and ensuring accuracy and consistency in project deliverables. From conceptual design to construction documentation, Revit serves as a comprehensive platform for architectural design and project management.
FAQs: Revit 2024 User Interface
Navigating the interface of Revit 2024 is essential for efficient project management and design. Let's get into common questions about Revit's user interface and explore detailed answers to each query.
What is the interface in Revit?
The interface in Revit refers to the graphical user interface (GUI) that provides users with access to various tools, commands, and functionalities within the software. It encompasses elements such as menus, toolbars, design bars, options bars, status bars, project browsers, and workspace view bars, all of which contribute to the user experience and facilitate efficient project management and design.
The interface serves as the gateway to Revit's vast array of features, allowing users to create, edit, and visualize architectural designs with precision and ease. By familiarizing yourself with the different components of the interface, you can navigate the software seamlessly and leverage its capabilities to bring your design concepts to life.
How do I access User Interface in Revit?
Accessing the user interface in Revit is straightforward and can be done upon launching the software. Once Revit is opened, the interface components will be visible on the screen, ready for interaction and utilization.
To navigate the interface effectively, start by familiarizing yourself with its various elements, such as menus, toolbars, and design bars. Experiment with different commands and tools to understand their functions and capabilities. Additionally, explore the options bar to adjust properties and settings as you work on your projects.
By actively engaging with the user interface and experimenting with its features, you'll gradually become more proficient in navigating Revit and harnessing its full potential for architectural design and visualization.
What is the name of the interface tool unique to Autodesk Revit?
One interface tool unique to Autodesk Revit is the Project Browser. The Project Browser serves as a navigation control within the software, allowing users to access and manage project views, sheets, schedules, families, and other project components.
Through the Project Browser, users can organize project elements in a hierarchical tree structure, making it easier to locate and manipulate specific items within the project. Whether you're navigating between different views or editing families, the Project Browser provides a centralized hub for efficient project management and organization.
What are some advanced features in Revit's interface?
In addition to the fundamental components of the interface, Revit offers several advanced features to enhance productivity and streamline workflow. One such feature is the Ribbon, which provides a contextual toolbar containing relevant commands and tools based on the selected task or object.
Another advanced feature is the Quick Access Toolbar, which allows users to customize and access frequently used commands and functions with ease. By adding commonly used tools to the Quick Access Toolbar, users can expedite their workflow and improve efficiency.
Additionally, Revit offers customizable keyboard shortcuts, allowing users to assign their preferred shortcuts to specific commands and tools. This feature enables users to navigate the interface more efficiently and perform tasks with greater speed and precision.
Furthermore, Revit's interface supports multi-monitor setups, allowing users to spread out their workspace across multiple screens for enhanced productivity and workflow management. By leveraging these advanced features, users can optimize their Revit experience and maximize their efficiency in architectural design and project execution.
Explore Further
Explore the following resources to deepen your understanding of CAD software and architectural fundamentals, essential for professionals, architecture students, and enthusiasts alike:
Free CAD Tutorials
- Computer Aided Design (CAD): Learn about various CAD software solutions offered by our team, a leading provider in the industry.
- Revit Free Training Tutorials: Access free tutorials provided by us to learn the basics of Revit, a powerful software for building information modeling (BIM).
- Revit Introduction-Modeling in 3D: Gain insights into 3D modeling techniques using Revit, enabling you to create detailed architectural designs.
- Revit Interface and Terminolog: Familiarize yourself with the interface and terminology used in Revit, facilitating smoother navigation and understanding of the software.
- AutoCAD Basics for Architects & Engineers: Explore the foundational concepts of AutoCAD, a widely used CAD software, tailored specifically for architects and engineers.
Architecture Fundamentals
- Architecture Design Process: Learn the importance of the design process in architecture, understanding the iterative stages involved in creating innovative designs.
- Architectural Presentation and Rendering: Learn about techniques and tools used for architectural presentation and rendering, enhancing your ability to communicate design concepts effectively.
